ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM-STRUCTURE- TYPES RETICULUM (ROUGH ER- SMOOTH ER) FUNCTIONS
Structure –Types And Functions Of Endoplasmic Reticulum
In the cytoplasm of the cell complex membrane bounded system is present. It was called cytoplasmic vacuolar system by "Sacz & De robertis" in 1975. This system contains endoplasmic reticule, nuclear envelop, and Golgi.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (E.R.) was first observed by "Porter, Claude, Fullam" in 1945.
Occurrence: In all eukaryotic cells E.R. is present. It is absent in R.B.C. of mammals and prokaryotes. In the embryonic cells E.R. is small. It is undifferentiated.
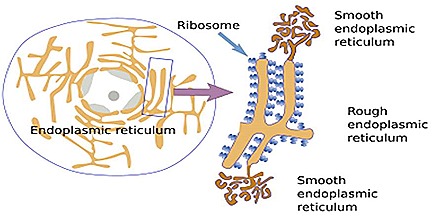
Types of E.R.: E.R. occurs in two forms a) Smooth E.R. b) Rough E.R.
Smooth E.R..- The E.R. without ribosomes is called smooth E.R. This is present in cells which synthesis steroids. In intestine cell, liver cells, retinal cells it is present.
Rough E.R: The E.R. shows ribosomes on its outer surface. They take up protein synthesis. This reticulum is more in protein synthesing cells.
Morphology: E.R. is represented in three forms; a) Cisternae b) Vesicles c) Tubules.
a) Cisternae : These are long unbranched flat structures. They are arranged parallely. They show 40 to 50 mill microns in diameter. They are more in liver pancreas, brain cells, etc.
b) Vesicles : They are oval membrane bounded structures. They are 25 to 500 mill microns in diameter. They occur in liver and pancreatic cells.
c) Tubules : They are small and branched. They show 50 to 190 mill microns in diameter. They are arranged irregularly in cell. They are seen in almost all the cells.
Electron microscopic structure of E.R.: All the three forms of E.R. will show double unit membranes. Each membrane shows 60 A0 thickness. The unit membrane show fluid mosaic nature of plasma membrane. Usually E.R. membrane is in contact with plasma membrane, nuclear membrane and Golgi. In 1965 "Palade" observed secretory granules in the E.R.
Biogenesis of E.R. : The origin and development of E.R. is not clearly
Known.
' l)From nuclear membrane: The membrane of E.R. resembles nuclear membrane and plasma membrane. Hence we believe that E.R. might have come from them.
2) E.R. Developed 'Denovo': It developed as it is.
3) Multistep mechanism: Rough E.R. is developed in the following way. a) Annulated lamellae: It was reported by "Meculloch" in 1952. From the nuclear membrane small structures are liberated as buds. They unite to form annulate lamellae. These lamellae are united to form cisternae. Thus E.R. is formed.
Functions:
1) Mechanical support: E.R. will give mechanical support to cytoplasm. Hence it is called cytoskeleton.
2) Intracellular transport: E.R. functions as circulatory system of the cell. It transport substance from one place to another place, in the cell it is called intracellular transport.
3) Protein synthesis : ER. will provide surface for the attachment of ribosomes. These ribosomes will synthesise the proteins.
4) Synthesis of lipoproteins : Smooth E.R. will synthesise lipids. In the Golgi complex the glycerides get associated with proteins produced by the E.R. Thus complex lipoproteins are formed.
5) Detoxification : Smooth E.R. will detoxify internal, or external toxins. If toxins are more in the body more smooth E.R. will be produced.
6) A.T.P. Synthesis : E.R. membranes are the sites of A.T.P, synthesis in the cell.
7) Formation of other membranes : In the cell E.R. gives rise to.
a) Cisternae of Golgi apparatus .
b) Outer membrane of nucleus.
8) impulse conduction : In the muscle sarcoplasmic eticulum will release calcium which is responsible for the muscle action In 1926 "Porter" stated that E.R. membrane shows ionic grandients, and electric potential.
Interrelationship of different cell membranes :
1) The outer membrane of the nucleus will give buds. They unite to form annulate lamellae.
2) Annulate lamellae will give rough E.R.
3) From smooth E.R. golgi will form.
4) Vesicles will give plasma lemma.
5)According to GERL system Golgi will give rise to primary lysosomes. Thus there is an interrelationship among the membrane systems.
