HIRUDINARIA-NERVOUS SYSTEM SENSE ORGANS
The nervous system of Leech is basically annelidan but it shows advancement over the other annelids. It shows central, peripheral and autonomic nervous systems.
1. Central nervous system:
It is enclosed in the venteral haemocoebmic canal. It shows.
i) Cerebral ganglia and nerve ring
ii)Nerve cord
iii) Terminal ganglionic mass
The ganglia are made by nerve cells.
i) Cerebral ganglia and nerve ring: On the pharynx in the fifth segment a pair of cerebral of supra' pharyngeal ganglia are present. They are fused. It is called brain.
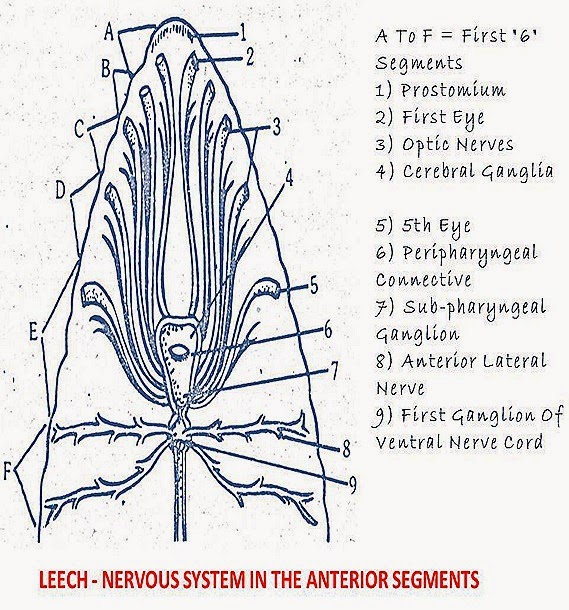
Below the pharynx in the fifth segment sub-pharyngeal ganglionic mass is present. It is formed by the union of the 4 pairs of ganglia.
The sub-pharyngeal ganglionic mass and cerebro (or) supra pharyngeal ganglionic mass will be connected by two circumpharyngeal connectives. Thus, a nerve ring is formed around the pharynx.
ii) Nerve cord: From the subpharyngeal ganglionic mass the nerve cord
starts. It runs backwards. It is mid ventral in position. It is present below the
posterior sucker. It wjll join the terminal ganglionic, mass present near the
posterior sucker.
The nerve cord shows 21 ganglia, one ganglion in the first annulus of each segment from 6th to 26th segments of the body: Each ganglion is formed by the union of 2 ganglia. They give nerves or peripheral nerves. The nerve cord is made by nerve cells and nerve fibres.
iii) Terminal ganglionic Mass: In the posterior sucker of leech
terminal ganglionic mass is present. It is the fusion product of 7 pairs of ganglia.
2. Peripheral nervous system: From the ganglia of the central nervous system many nerves will arise. These will constitute the peripheral nervous system.
i) One pair of nerves will arise from the front side of brain and go to first pair of eyes and prostomium.
ii) Four pairs of nerves arise from the sub-pharyngeal ganglionic mass. They go to 2, 3, 4, 5th pairs of eyes.
iii) Two pairs of nerves arise from each ganglion, and go to the body parts.
iv) Seven pairs of nerves will arise from terminal ganglionic mass and they go to posterior sucker.
3. Autonomic nervous system: Below the epidermis, in the muscles and on the wall of the alimentary canal nerve plexi are present. They join with peri pharyngeal connectives of the central nervous system. They also show connection with multipolar ganglionic cells present in the gut wall. Sensory Receptors of Leech :
In leech 4 kinds of sensory receptors are noticed. They are 1) Eyes 2) Free nerve endings 3) Annular receptors 4) Segmental receptors.
a) Eye: In leech 5 pairs of eyes are present, in the first 5 segments One pair of eyes in the first annulus of each segment. They are present on the dorsal side.
Structure:
Each eye is a cup like structure; it contains many large, light sensitive cells in vertical rows. Each cell contains a lens, and the cytoplasm is a thin layer.
Nucleus is pushed to one side. Each eye is covered on the free surface by cornea. Cornea is formed by transparent epidermal cells. Each eye is innervated by an optic nerve at the base.
Working:
It is not clearly known whether image is formed in the eye or not. Variation in the sizes of the Eyes :
i) The first and second pairs of eyes are largest.
ii)The fifth pair of eyes will be smallest.
Direction of the eyes:
i) The first pair of eyes will face forwards.
ii)The second pair of eyes will face forwards and outwards.
iii) The third and fourth pair of eyes will face backwards and outwards.
iv) The fifth pair of eyes will face backwards; because of this directional arrangement of eyes the animal can receive light rays from all sides.
b) Free nerve endings: All over the body these receptors are present. They are chemoreceptors. These are the nerve ends. These nerves will arise from the nerve cells present below the epidermis. They notice the chemical changes of the surroundings.
c) Annular receptors: In all the annuli of all the segments of the body of leech these receptors are present. They are tactile sense organs or they are called tangoreceptors. In each annuals roughly 36 annular receptors are present. The receptor is looking like papilla, it's base is connected with nerve fibre.
d) Segmental receptors : The segmental receptors are larger than the annular receptors. They are few in number. They are present in the first annulus of each segment. 4 pairs on the dorsal side and 3 pairs on the ventral side.
Each segmental receptor is papilla like structure with a group of tall, slender cells. In between the cells intercellular spaces are present. From the base of each cell a nerve fibril will arise. All the nerve fibrils will unite at the base of the receptor and becomes a nerve.
These receptors are tactile receptors. The dorsal segmental receptors work as tango and photoreceptors.
