DIGESTIVE GLANDS IN RABBIT
-
In the digestive system of rabbit, there are various digestive glands, which are situated either inside or outside the alimentary canal.
-
These glands produce secretion, which plays an important role for the digestion.
-
The glands which are situated outside the alimentary canal are salivary glands, liver and pancreas.
Salivary glands
These are mucous glands situated on the palate and tongue. Besides these mucous glands, there are also four pairs of salivary glands, situated around the buccal cavity. These are
i. Infraorbitals situated below the eye, and their ducts open near the upper molar.
ii. Parotids are at the base of external ears and through stensons duct open behind the upper incisor.
iii. Sublinguals are situated under the tongue and their short ducts open below the free part of the tongue,
iv. Submandibular or submaxillary glands lie on the inner side of the angles of lower jaws, through whartons duct open behind the lower incisors.
-
The salivary glands secrete saliva which is an alkaline juice containing mucilaginous mucin and watery ptyalin.
-
The function of ptyalin, which is an enzyme of ferment is to convert the starch into sugar.
-
Salivary glands produce their secretion by the process of reflex action caused due to the presence of food in the mouth.
Liver
-
It is the largest gland of the body, situated in the posterior concavity of the diaphragm with which it is connected by a peritoneal fold. Liver is five-lobed.
-
There are three lobes on the left side, while the other two lie on the right side.
-
The left lobes are left lateral, a left central and a spigelian lobe.
-
On the right side are located a right central and a caudate lobe. Gall bladder is a thin - walled, elongated sac, situated embedded in the groove of the right central lobe.
-
The function of the gall-bladder is to store the bile which is produced by liver.
-
Bile is greenish in colour, therefore, it also imparts the greenish colouration to the gall-bladder.
-
Bile is carried into the proximal part of the duodenum by a large common bile duct, which is formed by the joining of a cystic duct from the gallbladder and several small hepatic ducts from various lobes of liver.
-
Bile is an alkaline secretion which is responsible for emulsifying fats in the duodenum.
Pancreas
-
!t is an irregular gland made up of several, branching tubes ending in a blind secretory sac or acini.
-
Pancreas is held in the mesentery situated between the two limbs of the U-shaped duodenum.
-
It produces an alkaline secretion called pancreatic juice whicn is poured into the distal limb of the duodenum by the pancreatic duct.
-
Pancreatic juice possesses three enzymes called trypsin, amylase and lipase.
-
These enzymes act on the proteins, starches and fats respectively.
-
Between the secretory sacs or acini are situated several clusters of cells,
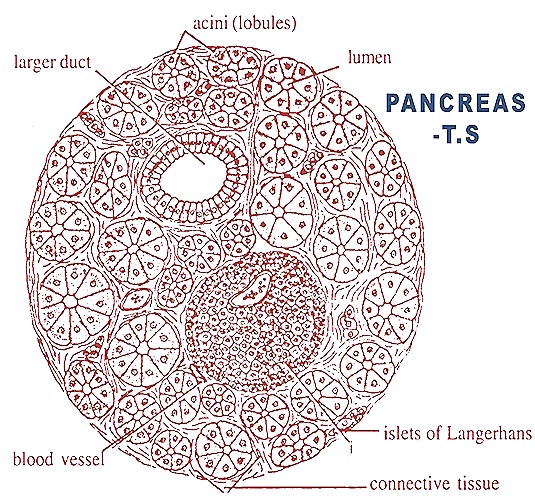
-
called islets of Langerhans. These are endocrine glands which produce a hormone knownas insulin.
-
It renders great effect to the metabolism of carbohydrates.
