FRESHLY LAID HEN'S EGG
The fully formed and freshly laid hen's egg is large. It is 3cm. in diameter and 5cm. in length. It contains enarmous amount of yolk. Such egg is called macrolecithal egg. The egg is oval in shape. The ovum contains a nucleus. It is covered by yolk free cytoplasm. It .is 3mm. in diameter. It is seen on the animal pole. The entire egg is filled with yolk. This yolk has alternative layers of yellow and white layers. They are arranged concentrically arround a flask shaped structure called latebra. Below the blastodisc the neck of latebra expands. This is called nucleus of pander. Yellow yolk got its colour because of carotenoids White yolk layers are thin and yellow yolk layers are thick. Yolk is a liquid. It contains 49% water and 33% phospholipids 18% proteins, vitamins, carbohydrates are present.
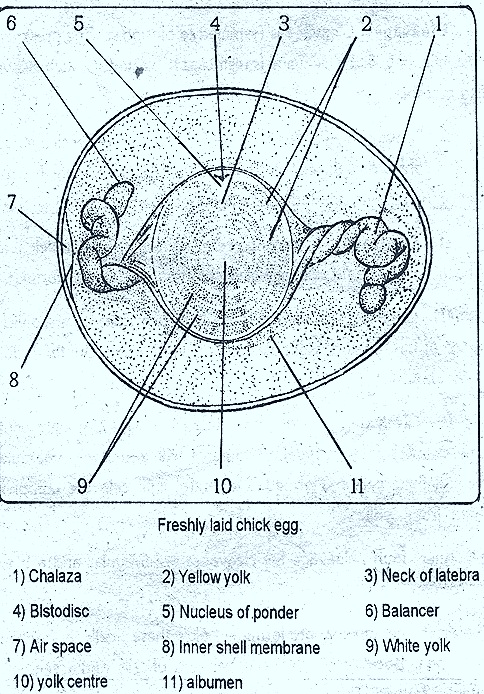
The entire ovum is covered by plasma membrane. It is called plasmalemma. It is lipoprotein layer. This is ovum is covered by egg membranes.
Primary membranes : These membranes develop between oocyte and follicle. The primary membranes are secreted by follicle cells. It is called vitelline,membrane is come from two origins. Inner part is produced by ovary. Outer part is from the falopian tube. (This is stated by Balinsky)
Secondary membranes : Oviduct secretes secondary membranes. Above vitelline membrane albumen is present. It is white in colour and it contains water and proteins. The outer layer of albumen is u.in.It is called thin albumen. The middle layer of albumen is thick. It is called thick albumen, or dense albumen. The inner most albumen is very thick. It develops into chalazae. The chalazae are called balancers. They keep the ovum in the centre.
Shell membranes : Above the albumen two shell membranes are present. Towards the broad end of egg, in between the shell membranes an air space is present. This air space is formed when egg is laid cooled from 60°C to lesser temperature.
Shell : Above the shell membranes a shell is present, it is porous in nature. It is calcareous. This porous shell is useful for exchange of gases. In a freshly laid hen's egg shell is soft. Very soon it becomes hard.

