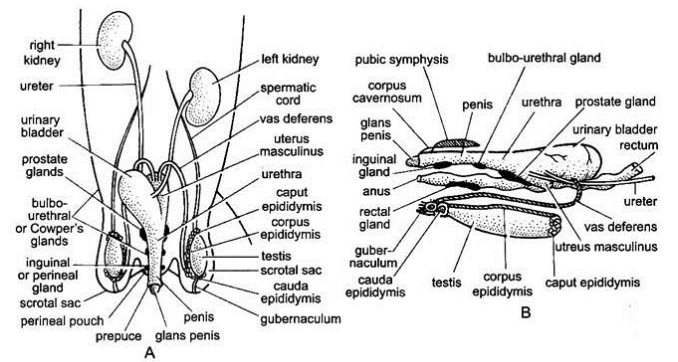
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OF RABBIT
In rabbit the sexes are separate i.e. unisexual and sexual dimorphism is well marked.
- The male reproductive organs include a pair of testes, a pair of epididymes, a pair of vasa deferentia, urethra, penis and some accessory glands.
1. TESTES
- The paired testes are small, ovoid bodies of light pink colour.
- Each testes lies in a special thin-walled sac of hairy skin outside the abdominal cavity, called the scrotum.
- It is located ventrally in the pubic region.
- In the foetus and new born rabbit, the testes lie within the abdominal cavity near kidneys where they were developed.
- But at puberty, they descend through inguinal canals into scrotal sacs.
- In most species of mammals the testes remain within scrotal sacs throught life.
- But in rabbit, rat and other rodents, they are migratory. They descend into the scrotum during the breeding season, but withdraw into the abdominal cavity during non-breeding periods through inguinal canals which remain open throught life.
- The reason for this is spermatozoa can develop within the scrotalsacs at low temperature but cannot develop inside abdomen at normal temperature.
- Histologically, the mammalian testis is composed of a number of wedge-shaped or cone-shaped compartments or locules.
- The outer protective covering of testis, the tunica aibuginea, is a tough capsule made of white fibrous connective tissue, which projects inwards forming interlobular septa.
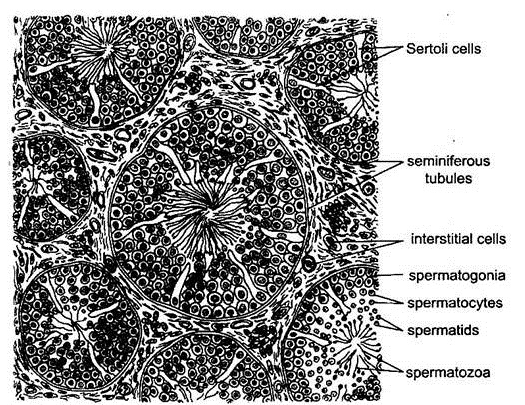
- Each lobule contains long, slender, much convoluted microscopic seminiferous tubules bound together by connective tissue.
- The germinal epithelium lining of the tubule is made of two kinds of cells.
- The most numerous are the smaller spermatogenic cells which undergo spermatogenesis to produce spermatozoa.
- A few larger, tall, columnar supporting cells, called Sertoli cells, nourish the sperm cells before they leave the tubule.
- Each sperm consists of a head composed mainly of the nucleus, and a long cytoplasmic tail.
- In the connective tissue between the seminiferous tubules lie scattered the interstitial cells or the cells of Leydig which are endocrine in function.
- All the seminiferous tubules in each testis open into a network called rete testis.
- It opens by several fine ductules lined by cilia, called vasa efferentia, into the epididymis.
- The spermatozoa produced by testis are transferred through vasa efferentia into the epididymis.
2. EPIDIDYMIS
- The epididymis is an irregular, narrow and highly convoluted tubule of great length.
- It forms a compact ridge - like mass all along the inner surface of the testis.
- The epididymis has three distinct parts.
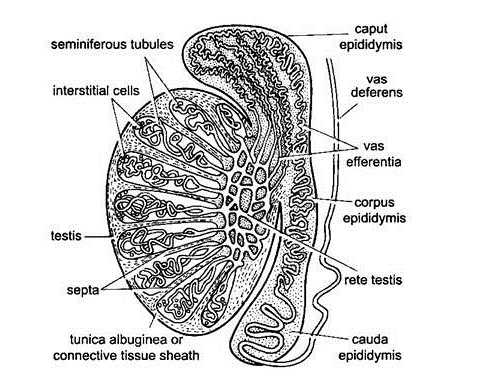
A.CAPUT EPIDIDYMIS:
- It is the head or anterior part which is connected with the anterior end of the testis through vasa efferentia. It lies buried in the fat body.
- It is also connected with the dorsal abdominal wall by a spermatic duct consisting of connective tissue spermatic artery, spermatic vein and a nerve.
- The vein forms an extensive capillary network round the artery called the pampiniform plexus.
B.CAUDA APIDIDYMI:
- It is the tail or posterior part which connects the posterior end of the testis to the scrotal sac by a thick elastic cord of connective tissue, called the gubernaculum.
- When it shortens, it draws the testis into the scrotal sac.
C. CORPUS EOHLIDYMIS:
- It is the narrow body or middle part connecting the caput and the cauda epididymis.
3.VASA DEFERENTIA
- The basal end of each epididymis (cauda epididymis) leads into a yellowish-white, straight, and muscular tube, the sperm duct or vas deferens.
- It runs forward along the inner side of the scrotal sac, traverses the inguinal canal to enterthe abdominal cavity.
- It loops ventrally under the ureter and opens dorsally into urethra immediately in front of the opening of the ureter.
- A small slightly bifurcated blindsac, uterus masculinus or seminal vesicle, opens dorsally into urethra just dorsal to the openings of vasa deferentia.
4.URETHRA
- The neck of the urinary bladder and the vasa deferentia open into a thick-walled muscular duct, the urethra. It is the common passage for both urine and semen and called the urinogenital duct.
- It traverses and opens at the tip of the penis as the male urinogenital aperture.
5.PENIS
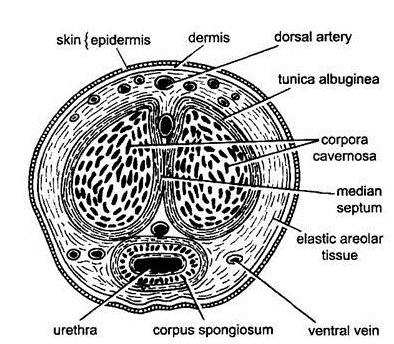
- The copulatory organ or penis is a small, cylindrical and erectile organ in front of the anus.
- It is composed of three longitudinal columns of spongy erectile tissue, which become filled with blood during sexual exitement to produce erection of penis.
- Surrounding the urethra is corpus spongiosum above which lie the two corpora cavernosa.
- The penis is enclosed in a sheath of skin which hangs loosely as a fold over its cap-like tip known as prepuce.
- The penis serves to transmit sperms into the vagina of the female during sexual intercourse.
- The operation of circumcision is the removal of the prepuce.
6 . ACCESSORY SEX GLANDS
- Several accessory sex glands open into urethra of male.
- Their secretions, together with those of epididymes and uterus masculinus, constitute the seminal fluid or semen.
A.PROSTATE GLAND
- A large prostate gland lies dorsally around the base of uterus masculinus.
- It opens into urethra by several small ducts. Its whitish alkaline secretion activates the passive spermatozoa.
B. COWPER GLAND
- A pair of Cowper's glands lie posteriorly to the prostate glands dorsally at the base of penis.
- Their secretion neutralizes acidity for the protection of spermatozoa.
C.PERINEAL GLANDS:
- These are a pair of dark elongated scent glands lying behind the Cowper's glands.
- As mentioned earlier, they open into the hairless perineal depressions one on either side of anus.
- Their odorous secretion gives the rabbit its characteristic smell.
D.RECTAL GLANDS:
- A pair of rectal glands of unknown function is situated dorsally on the rectum.
