HERDMANIA TADPOLE LARVA
ORGANISATION OF HERDMANIA TADPOLE LARVA:
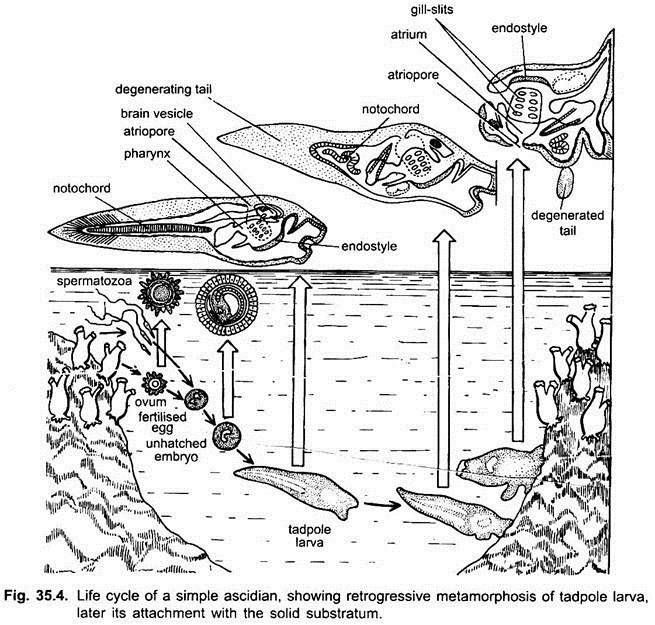
Herdmania is a hermaphrodite animal. The fertilised eggs undergo holoblastic unequal clevage and it develops into blastula. it shows upper micromeres and lower macromeres. By invagination of the macromeres gastrulation takes place and gastrula is formed. This gastrula develops into a tailed larva called Ascidian Tadpole larva. (Herdmanis life history, is not clearly known. Clavilina’s life history is known. It is followed here.
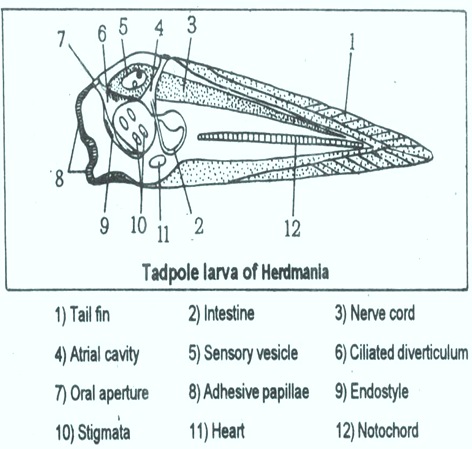
The larva is 3 mm in length. It has short oval body and a long tail.
This larva shows all the chordate features.
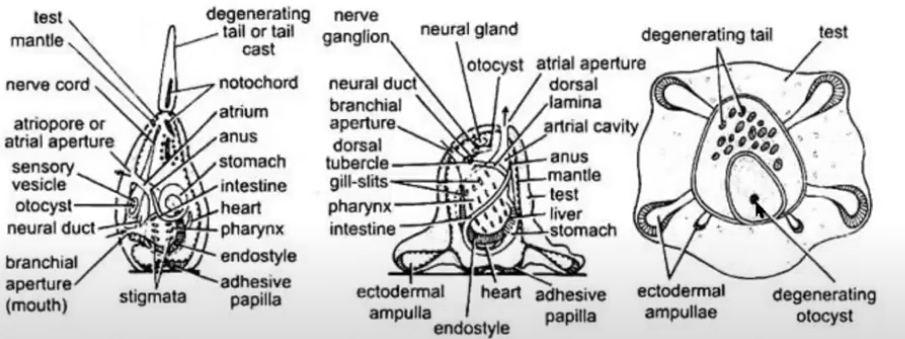
1) The body is covered by thin test.
2) The tail is long and shows a tail fin or caudal fin.
3) The tail is supported by notochord. Hence it comes under urochordata.
4) On the dorsal side above the notochord hollow nerve cord is present. This nerve cord is enlarged at the anterior end as a cerebral vesicle. In the cerebral vesicle pigmented eye spot is present. Statocyst is also present. They work as sense organs.
5) On either side of the notochord in the tail region muscles are Present which are helpful in the locomotion.
6) On the trunk region digestive system is present. It shows large pharynx with few gills slits. They open into atrium. On the mid ventral floor of the pharynx an endostyle is present.
7) Atrium opens out through atriopore.
8) Below the pharynx on the ventral side a muscular heart is present.
9) On the anterior end of the trunk three adhesive papillae are present These are very much useful to attach the larva to the substratum
This Herdmania tadpole larva shows all chordate characters. This larvae ‘undergoes retrogressive’ metamorphosis and develops into adult Herdmania.
Life Cycle of Herdmania
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Fertilized Egg | Holoblastic unequal cleavage → Blastula |
| Gastrula | Formed by macromere invagination |
| Tadpole Larva | Free-swimming, chordate features (notochord, nerve cord) |
| Attachment | Via adhesive papillae |
| Metamorphosis |
Retrogressive: loss of notochord & sense organs |
| Adult Herdmania | Sessile, filter-feeding ascidian |
Retrogressive Metamorphosis in Herdmania
| Feature | In Larva | In Adult |
|---|---|---|
| Locomotion | Tail with muscles | Sessile |
| Notochord | Present in tail | Absent |
| Nerve Cord | Hollow, dorsal, cerebral vesicle | Reduced nerve ganglion |
| Sense Organs | Eye spot, statocyst | Lost |
| Pharynx | Small with few gill slits | Enlarged with pharyngeal basket |
| Adhesive Organs | Papillae for substrate binding | Lost after attachment |