CHICK-EXTRA EMBRYONIC MEMBRANES
FOETAL MEMBRANES OF CHICK
In amniotes the developing embryo in order to grow properly foetal membranes are formed.
When few membranes are produced by mother, it should take more care for their survival. If the number are more, care will be less. In amniotes when the developing embryo is enveloped, by extra embryonic membranes, which will give scope, for developing embryo, the extra embryonic membranes are chorion, amnion, yolk sac, allantois.
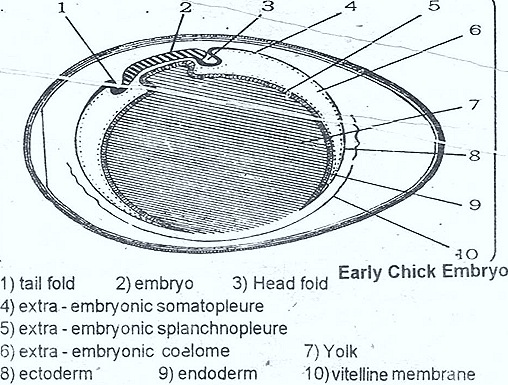
In the development of chick these membranes will develop from orginal blastoderm, the central part of blastoderm will give embryo proper, the marginal blastoderm will give extra embryonic membranes amnion and chorion will develop from somatopleurae, yolk sac and allontois, will develop from spiafichnopleurae.
Amnion & Chorin : In the development of embryo amnion and chorion are closely associated, Amnion is bag like covering over'the em¬bryo, it separates the embryo from internal environment, Amnion is deveU oped from somatopleuric amniotic folds. These folds are head fold, lateral folds and tail folds.
a) At about 30 hours of incubation, in front of the head of embryo a head fold is developed, it is called amniotic head fold.
b) At about third day of incubation amniotic tail fold is developed. It grows opposite to head fold.
c) Mean while lateral folds will develop, they grow dorsomedially.
d) After some time head fold, lateral folds, and tail fold will fuse near posterior end of a embryo.
e) At 72 of incubation they are still not fused. They show an opening called amniotic umblicus, afterwards they unite.
f) After their union at the point of union "sero-amniotic raphae" is present. It is a fold.
g) Because of this union outer chorion inner amnion will form, because it is developed from somatopleure. In chorion ectoderm is present out side and mesoderm is present inside. In amnion ectoderm is inside, mesoderm is out side. Hence the space between amnion and chorion is called exocoel or extraembryonic coelome.
Functions of chorion :-
1) The extra embryonic coelome is filled with a fluid. It gives protection to the developing embryo.
2) This coelome gives space, for developing allantois.
3) Chorion combines with allantois and acts as a respiratory organ.
Functions of Amnion :
Amnion is sac like structure around embryo. It contains amniotic fluid. It will protect embryo from mechanical shocks and dessications.
It protects the embryo when the egg is laid. It gives artificial aquatic environment for growth of embryo. Yolk sac :
At 16 hours of incubation, yolk sac makes its appearence.
It develops from Splanchanopleurae Splanchanopleurae contains Endoderm and mesoderm layers.
The Splanchanopleuraeinstead of forming a close gut, it will grow over yolk, and becomes yolk sac.
The primitive gut is present above the yolk. This yolk region is in contact with midgut. Finally the yolk sac is communicated with midgut through an opening.
Functions of Yolk sac :
It digests the yolk, and the digested food will be circulated through blood to the developing embryo. Hence yolk sac is considered as a nutritive organ of the embryo.
Allantois :
In chick it develops from the ventral part of caudal end of the hindgut. It develops at third day of incubation. It develops from SplanchanopleuraeThisSplanchanopleuraecontains endoderm and meso¬derm, the allantois grows rapidly, and occupies the entire exocoel. The mesoderm of thechorionand mesoderm of allantois will unite. It forms chrio allantoic membrane.
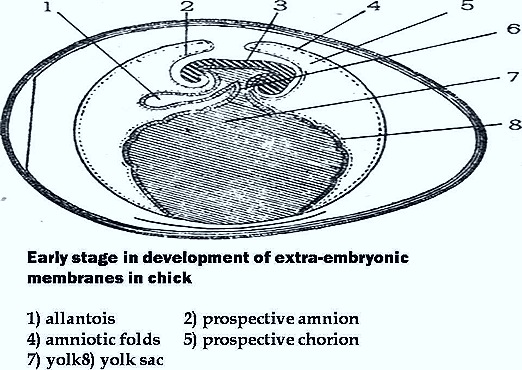
Allantois is connected to the hindgut, and is called as allantoic stalk.
As the embryo is growing the allantoic and yolk stalk are brought together. Their mesodermal layers will unite. It is called umblical stalk. It is covered by somatic umblicus.
Functions of Allantois :
Allantois is richly vascularised. Hence it works as respiratory organ.
It stores nitrogenous waste material of the embryo.
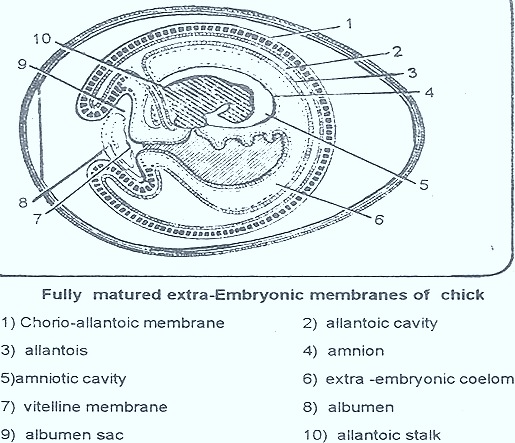
In later development the allantoic circulation will absorb calcicum from the shell. This calcium is used in construction of bones in young ones.
Allantois absorbs calcium from shell. Hence the shell becomes thin. It helps in rupturing the shell during hatching.
