MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OF BIRD-RABBIT-REPTILE-COMPARISION
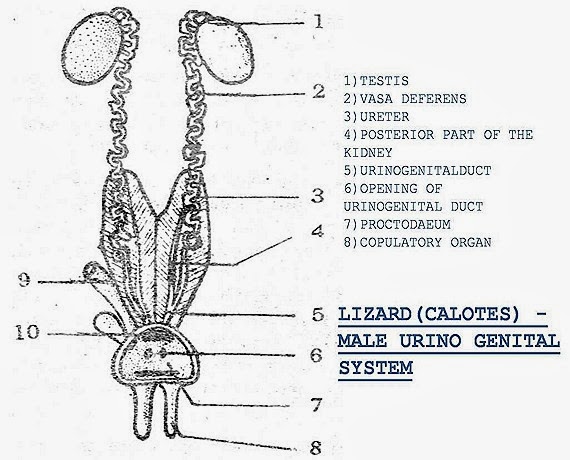
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OF LIZARD (CALOTES)
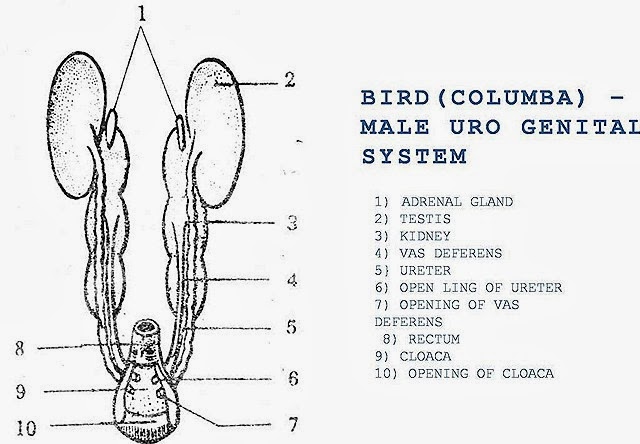
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OF PEGION ((COLUMBA)
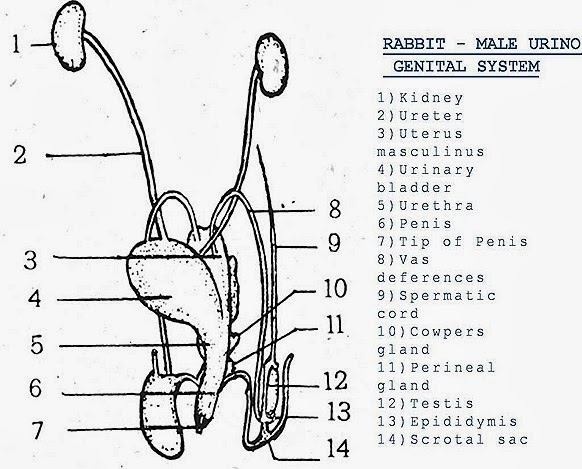
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OF MAMMAL ((RABBIT- ORYCTOLAGUS)-COMPARITIVE ANATOMY
THE FOLLOWING TABLE AND IMAGES CLEARLY
shows the similarities and differences between male urino genital system of lizard-bird-mammal.
| MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OF CALOTES (GARDENLIZARD) | MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OFCOLUMBA (PIGEON) | MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OFORYCTOLAGUS (RABBIT) |
| 1. Testes are white ovoid bodies. | 1. Testis white ovoid bodies. | 1. Testes are pink, ovoid bodies. |
| 2. Testes lie in the abdominal cavity much ahead of kidneys. Inguinal canal is absent. | 2. Testes lie in the abdominal cavity under the anterior parts of kidneys. Inguinal canal is absent. | 2. Testes are extra abdominal and lie in the scrotal sacs which are the folds of the skin. They are connected with perivisceral cavity by inguinal canals. |
| 3 Right testis is a little ahead of the left one. | 3. Left testis is a little bigger than the right one. | 3. Right and left testes are symmetrical. |
| 4. Spermatic cord is not formed. | 4. Same as in calotes. | 4. A spermatic cord extends from each testis to a little behind the kidney of its side. |
| 5. Each testis is attached to the dorsal body wall by a double fold of peritoneum the mesorchium. | 5. Each testis is attached to the kidney of its side by mesorchium. | 5. Each testis is attached to the wall of scrotal sac by a short, thick, elastic cord 'gubernaculum'. |
| 6. From the inner end of each testis arises a much convoluted tube-epididymis. | 6. Epididymis is absent. | 6. Epididymis is present. |
| 7. Caput and cauda epididymis are not found | 7. Same as in calotes. | 7 Caput epididymis and cauda epi-didymes are the extensions of epididymis infront and behind the testis |
| 8. Epididymis is continued behind as long, narrow, coiled and delicate vas deferens. It passes backwards along the ventral surface of the kidney of its side and joins with the ureter to form urino-genital sinus which opens into the cloaca. | 8 The vas deferens arises directly from the inner border of the kidney in the form of a narrow convolutec tube. It runs backwards outside the ureter parallel to it and both open dorsally by separate aperture in urodaeum of the cloaca. | 8. The vas deferens passes through the inguinal canal and runs forward and enters into the abdominal cavity. So that a loop around the ureter of its side to open into sac-uterus masculinus' which is present in the dorsal wall of the urinary bladder. |
| 9. Seminal vesicles are absent. | 9. Posterior end of each vas deferens enlarges to form seminal vesicle. | 9. Seminal vesicles are absent. |
| 10. There are no special glands associated with male genital system. | 10. Same as in calotes. | 10. There are prostate, couper's and perineal glands are associated with the male genital system. |
| 11. In male a pair of eversible copulatory organs 'hemipenes' lie under the skin behind cloacai aperture | 11. Copulatory organs are absent. | 11. The copulatory organ in male is in the form of a thick muscular 'Penis'. It is covered by skin loose fold prepuce or foreskin penis is made up of a spongy tissue containing bbod vessels and it is erectile. |
previous topic is frog reproductive system-fish reproductive system-comparison
