SYCON SPONGE-REPRODUCTION
REPRODUCTION TYPES IN SYCON SPONGE
Sycon shows two types of reproduction namely.
I. Asexual reproduction
II.Sexual reproduction
I. Asexual reproduction : Sponges show asexual reproduction by the following methods:
(1) BY BUDDING (2) BY REGENERATION,
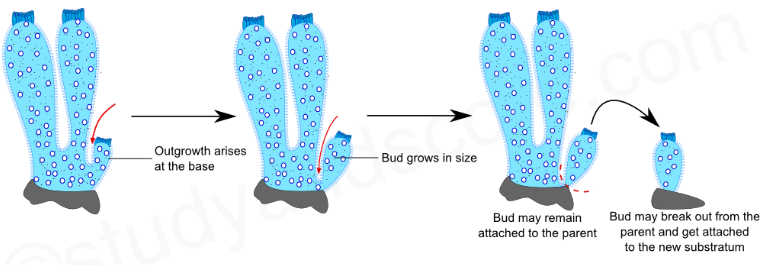
1) Budding : The body of sycon is highly branched. When the conditions are favorable small projections arise from the basal region of the adult sponge. A small projection grows and develops into a small bud. After some time the bud separates from the body of the parent. When it comes in contact with a substratum it attaches to a substratum and develops into an independent animal.
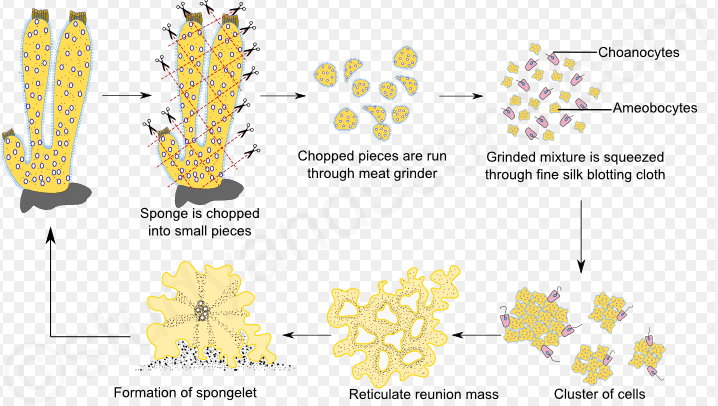
2) Regeneration : Sycon shows the power of regeneration to a remarkable extent. By accident the sponge body becomes cut into pieces, each piece develops into a young & complete sponge. This process is called regeneration.
II. Sexual reproduction : Sycon is a hermaphrodite animal. In the same animal both male and female sex cells will develop.
Sperm : An 'archaeocyte enlarges in -size and functions as sperm mother cell. This is covered by flat cells. Then the sperm mother
a) cell undergoes divisions and spermatocytes are formed. They develop into sperms. Each sperm has a tail.
b) Ova : An archaeocyte enlarges and functions as a egg mother cell. This cell gets its food supply from nurse cells. The egg mother cell undergoes two divisions and ovum is formed.
Fertilization :Along with incurrent water sperms enter the body of a sponge and unite with ovum Zygote is formed;.
Cleavage :The zygote undergoes holoblastic unequal cleavage. The blastula is called Stomoblastula.
Stomoblastula shows micromeres with flagella which face the blastocoel. The large cells remain undivided for a long time. In the middle of this region of large cells a mouth opening is formed This stage is called stomoblastula by Tuzet'.This stomoblastula undergoes an inversion through the mouth and Amphiblastula is formed.
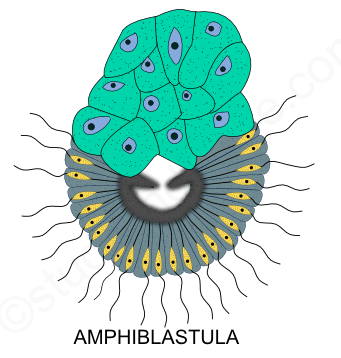
Amphiblastula larva : is the larva of sycon. It is oval in shape. It shows small micromeres with flagella on one side. This other half of the larva shows large macromeres. This larva comes out of the sponge through the osculum. It swims in water for some time with the help of flagella. Then it undergoes metamorphosis.
Metamorphosis :The macromeres will over grow the micromeres and thus gastrulation takes place. Flagellated cells become internal. It attaches to a substratum.
The outer layer develops into derma! layer. The inner layer of flagellated cells will develop into gastral layer. Then in between the two layers mesenchyme is developed. Thus a young sponge is developed.
