Organic Evolution Evidences
EVIDENCES OF ORGANIC EVOLUTION
The theories which we have discussed are imaginary. There is no practical proof for them. The various animals which we are seeing to-day were gradually evolved from simple past lived organisms. It is not possible for anybody to observe a single change, because our life span is too short. Hence scientists collected evidences from different branches of biology. They are,
1. Morphological and anatomical evidences.
2. Embryological evidences
3. Paleontological evidences.
4. Physiological evidences.
5. Zoo geographical evidences.
MORPHOLOGICAL AND ANATOMICAL EVIDENCES
In all the living organisms, the structural and functional units are cells. If all the living organisms were created by super natural power, why he created same cells in all living organisms? If we observe the shape of Chimpanzee and man, there is a great similarity. Why? Even if we observe the fore limbs of different vertebrates, there is a similarity. Why? If we observe the brain of different vertebrates, there is a similarity in structure and function. Why? All the above questions indicate that there is a relationship between the organisms.
The organs of different individuals are classified into three types. They are homologous, analogous and vestigial organs.
1. HOMOLOGOUS ORGANS
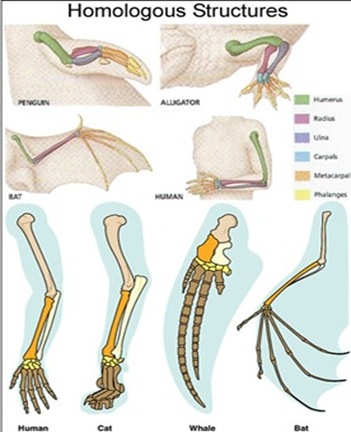
The organs which have common origin and structure are called homologous organs.
C. Example - iii: Vertebrae of different vertebrates.
D. Example - iv: Hind limbs of different vertebrates.
E. Example - v: Thorn of Bougainvillea and tendril of Cucurbit.
F. Example - vi: The brain of different vertebrates.
G. Example - vii: The wings’ of Bat and Bird.
H. Example -viii: The appendages of prawn explain serial homology.
ANALOGOUS ORGANS
The organs which have common form and function are called analogous organs. But they must differ in origin and structure.
A. Analogous organs-Example-I
The wings of Insect and Bird. In both the wings perform flying.But the wing of Insect is derived from ectoderm and it is supported by chitinous nervures. Whereas the wing of Bird is derived from mesoderm and it is supported by bones.
The above explanation tells us that the Insect and Bird had different ancestors. Probably the acquatic Annelid when entered into air, it evolved into lnsect.The terrestrial Reptile when entered into air, it evolved into Bird.
CONVERGENT EVOLUTION:
It is explained by analogous organs.When the different animals (Annelid,Reptile) of different habitats (Water,Iand) entered into the same habitat (air), they evolved into different animals (lnsect,Bird). It is called Convergent evolution
B. Example -ii: Scales of Fishes and Reptiles.
C. Example-iii:
Tubers of seweet potato and vegetable potato.
When different animals are living in the same habitat, they contain same shape. So, analogous organs have same shape. For example Fish and Whale contain same shape as both are living in water The shape of Earthworm and Snake is same as both live in burrows.
VESTIGEAL ORGANS
The organs which are non functional and reduced in an organism are called vestigial organs. But these organs were well developed and performed functions in ancestors. The organs become functionless when the animals enter into new habitat or when their function is taken up by another organ or when the habits are changed. Presence of vestigial organs is the most convincing evidence in favour of
organic evolution and is also supported by the disuse principle of Lamarck.
A. Vestigial organs of Man:
B. In man there are nearly 180 different types of vestigeal organs. Hence Welder Sheim described human being as moving museum of variable antiquities.
The different vestigeal organs of man are Vermiform appendix Coccyx, Nictitating membrane (plica semilunaris), Muscles of Ear pinna , Clitoris of female human being etc.
B. Vestigeal organs of Ratitee Birds: Wings
C. Vestigeal organs of Python and Whale: hind limbs
D. Vestigeal organs of Horse: splint bones of limbs.
E. Atavism:
Formation of all ready disappeared organs suddenly in an individual is called atavism. Such organs are called atavistic organs. These support organic evolution. If human baby born with tail, the tail is considered as atavistic organ.
If human baby born with many pairs of mammary glands, except one pair other pairs are considered as atavistic organs.
4. CONNECTING LINKS
The organisms having the structures of two different groups are called connecting links. These explain the path of evolution . The connecting links are
A. Peripatus: It consists of nephridia like annelids and trachea like arthropods. Hence peripatus is considered as living connecting link between annelids and arthoropods. We can also say that annelids evolved into arthropods through the peripatus.
Annelids -------------------- peripatus ---------------> Arthropods.
B. Monotremes (prototherians-Echidna, Ornithorynchus):
These lay eggs like reptiles and contain mammary glands like mammals. Hence monotremes are considered as connecting inks between reptiles and mammals. We can also say that the reptiles evolved into mammals.
